Report Source: Gartner Magic Quadrant for Digital Commerce
Publication Period: 2024-2025
Market Coverage: 19 Digital Commerce Platform Vendors
Analysis Date: January 30, 2026
Executive Summary
This critical analysis examines Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for Digital Commerce, a research report evaluating 19 vendors in the digital commerce platform market. The report reveals a maturing market experiencing 14% year on year growth, reaching $10.2 billion in software revenue in 2024 (Gartner, 2024). The analysis identifies artificial intelligence, composable commerce architectures, and B2B portal capabilities as key market differentiators, while highlighting persistent challenges around platform migration complexity and quantifiable ROI demonstration.
Market Context and Methodology Assessment
Market Size and Growth Trajectory
The digital commerce platform market demonstrates robust expansion despite macroeconomic headwinds. Gartner reports that the market achieved $10.2 billion in software revenue during 2024, representing a 14% year on year increase compared to 11.2% growth in 2023 (Gartner, 2024). This acceleration is noteworthy given concurrent geopolitical tensions and enterprise budget scrutiny that typically suppress technology spending.
The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) forecast of 14.3% in constant currency through 2029 positions digital commerce as a high growth segment within the broader CRM ecosystem, which is projected at 14.8% CAGR over the same period (Gartner, 2024). However, this optimistic projection warrants skepticism given several countervailing factors: potential recession risks, ongoing geopolitical instability, and the natural market saturation as digital commerce adoption approaches maturity in developed economies.
Inclusion Criteria and Market Representation
Gartner’s decision to raise the revenue threshold from $20 million to $28 million for vendor inclusion reflects genuine market consolidation and vendor growth. This 40% increase in the entry barrier suggests that smaller, niche players are either scaling rapidly or being acquired, indicating a maturing market with rising barriers to entry. However, this methodology creates blind spots: the report acknowledges tracking “160-plus other vendors” not included in the analysis, raising questions about whether the 19 evaluated vendors truly represent innovation occurring across the broader ecosystem.
The research explicitly focuses on vendors demonstrating “future growth potential” through architectural innovation and visionary strategy. While forward looking, this approach may undervalue vendors with strong current capabilities but conservative roadmaps, potentially misleading buyers seeking stable, proven solutions over cutting-edge but unproven features.
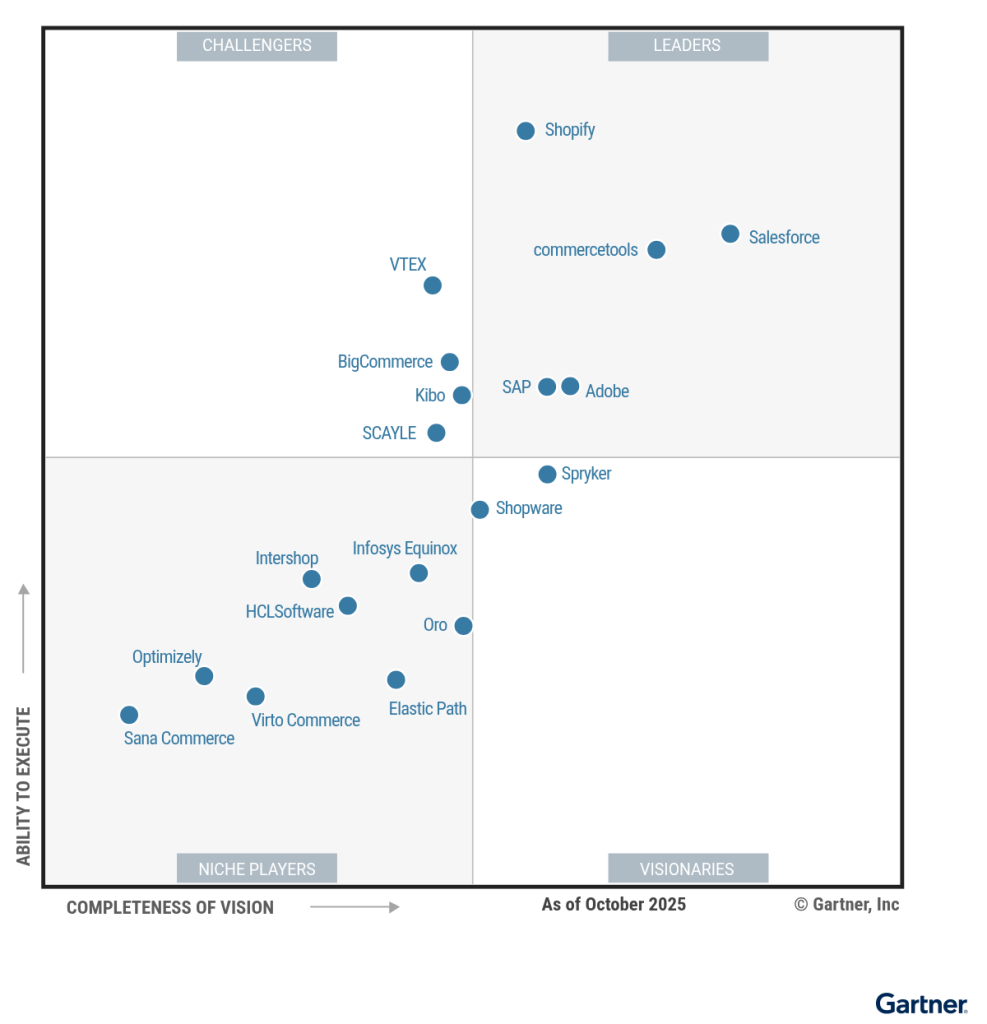
Strategic Technology Trends Analysis
Artificial Intelligence Integration: Hype Versus Reality
The report positions AI as a central differentiator, with “remarkable progress in AI capabilities” observed across customer experience enhancement, employee workflow optimization, and development acceleration (Gartner, 2024). However, the analysis reveals a critical gap between AI deployment and business value measurement. Gartner acknowledges that “effectively measuring and connecting these technological advancements to specific business outcomes” remains the central challenge facing the industry.
This disconnect between AI implementation and quantifiable ROI represents a significant risk for buyers. Adobe’s positioning as a Leader is tempered by the caution that its “commerce-related AI agents are mostly in development, while competitors offer more generally available agentic AI features today” (Gartner, 2024). This suggests that even market leaders struggle to operationalize AI beyond experimental or limited-scope deployments.
The emphasis on “agentic commerce” and “agent orchestration platforms” in vendor roadmaps appears aspirational rather than operational. The lack of concrete business outcome metrics for AI features across vendor profiles suggests the market remains in the experimentation phase, with production ready, ROI-positive AI implementations still emerging.
Composable Commerce Architecture: Promise and Complexity
The report highlights the “ongoing shift toward composable commerce” driven by promises of increased agility through modularity (Gartner, 2024). BigCommerce’s recognition as a Challenger is explicitly attributed to its “modular, API-first, cloud-native architecture” that aligns with technically sophisticated buyers seeking best-of-breed composition.
However, the analysis acknowledges that organizations simultaneously “navigate more complex architectures and contractual relationships” when pursuing composability. This represents a fundamental tension: composable architectures theoretically increase agility but practically introduce integration complexity, vendor management overhead, and potential performance bottlenecks across distributed systems.
The report’s assertion that “AI further amplifies this agility by streamlining integration, automating processes and enabling rapid adaptation” appears optimistic given the earlier acknowledgment that measuring AI’s business impact remains problematic. If organizations cannot reliably quantify AI’s value in simpler contexts, its contribution to composable architecture management is likely overstated.
Vendor Landscape Critical Evaluation
Leaders Quadrant: Adobe’s Dual Platform Dilemma
Adobe’s classification as a Leader is supported by strong product portfolio synergy, particularly native integrations with Adobe Experience Manager Assets, Firefly, and Express (Gartner, 2024). However, the report identifies a significant structural weakness: Adobe must “maintain both PaaS and SaaS platforms until customers fully transition to the SaaS environment” with “no end of support communicated for its PaaS/on-premises platform.”
This dual-platform maintenance creates several critical risks for Adobe customers:
- Resource Fragmentation: Engineering resources divided between fundamentally different infrastructures may slow innovation velocity on both platforms
- Feature Parity Uncertainty: The absence of clarity on feature availability, support levels, and update cadence across platforms creates decision paralysis for customers considering migration
- Migration Complexity: Despite offering migration tools, customers report “difficulty staying current with new releases” and frustration over upgrade “cost and complexity” (Gartner, 2024)
The upgrade challenges cited by customers, compatibility issues with third-party extensions, substantial resource requirements, time consuming processes, suggest Adobe’s extensibility model creates technical debt that compounds over release cycles. While Adobe positions its new Commerce as a Cloud Service as addressing these concerns, the lack of proven migration paths at scale represents execution risk.
Challengers and Niche Players: Market Positioning Analysis
BigCommerce’s Challenger positioning reflects its success in serving midmarket and growing enterprise B2B segments, with particular strength in multisite and localization capabilities. However, the geographic concentration in North America and Europe, combined with a customer base predominantly generating less than $10 million in gross merchandise value, suggests limited proven scalability for global enterprise deployments.
The evaluation criteria’s emphasis on “architectural innovation” and “visionary strategy” may inadvertently favor vendors with compelling roadmaps over those with battle-tested implementations. This methodology bias could mislead buyers who prioritize operational stability and proven scale over innovative but unproven capabilities.
Mandatory and Common Features Assessment
Core Capability Expectations
The report establishes mandatory features including self-service commerce experiences, product discovery and cart management, business tooling for merchandising and catalog management, and API-based interoperability (Gartner, 2024). These baseline requirements reflect market maturity—vendors unable to deliver these capabilities have already exited the competitive set.
More revealing are the “common features” listed, including B2B-focused capabilities, marketplace operations, and basic implementations of adjacent technologies (contact center, PIM, OMS, CPQ, CDP). The qualifier “basic” repeatedly appears, suggesting these extended capabilities often lack the depth required for enterprise production use. Buyers should scrutinize whether vendors’ extended feature sets genuinely eliminate the need for specialized point solutions or merely check boxes for RFP compliance.
Content Management System Integration
The report identifies “growing emphasis on robust, native content management systems” with “sophisticated CMS capabilities integrated directly into their platforms” including “intuitive visual page builders” (Gartner, 2024). This trend reflects the maturation of headless commerce architectures, where the CMS serves as the presentation layer decoupled from commerce logic.
However, the analysis does not address whether vendor native CMS capabilities genuinely compete with specialized content management platforms or represent minimally viable implementations. Organizations with complex content requirements spanning multiple channels and markets should validate whether native CMS offerings truly eliminate the need for best-of-breed content platforms versus introducing compromise solutions.
B2B Commerce Evolution and Customer Portal Significance
The report highlights B2B commerce as a critical growth area, noting vendors increasingly recognize the importance of “comprehensive customer portals designed to support the full spectrum of postsales interactions” beyond transactional capabilities (Gartner, 2024). This includes self-service experiences for service requests, claims management, order tracking, and personalized support.
This evolution represents a fundamental shift from viewing digital commerce platforms as purely transactional systems to comprehensive customer engagement hubs. The emphasis on “end-to-end B2B relationships” and “entire customer life cycle” support positions commerce platforms as potential replacements for traditional customer relationship management and service management systems.
However, the analysis lacks examination of organizational readiness for this expanded scope. Successfully deploying comprehensive customer portals requires cross-functional alignment spanning commerce, customer service, logistics, and account management teams—organizational changes potentially more complex than the underlying technology implementation.
Strategic Planning Assumption Critique
The report’s strategic planning assumption projects that “by 2028, 75% of B2B organizations will complete their highest revenue deals via digital channels” (Gartner, 2024). This aggressive forecast warrants critical examination:
Supporting Factors:
- Accelerated digital adoption driven by pandemic-era necessity
- Improved user experience parity between consumer and business commerce
- Enhanced self-service capabilities reducing transaction friction
- Mobile and remote workforce preferences favoring digital channels
Contradicting Realities:
- High-value B2B transactions often involve complex negotiations, customization, and relationship based selling that resist full digitization
- Many industries maintain regulatory, contractual, or organizational requirements for human involvement in large transactions
- The assumption conflates “completing” transactions digitally with “initiating” or “influencing” them digitally, the latter is more plausible
The 75% threshold appears optimistic without clarification on transaction value thresholds, industry segmentation, and the definition of “completing” deals. Organizations should plan for increased digital channel importance while maintaining robust assisted-selling capabilities for complex, high-value opportunities.
Market Dynamics and Competitive Pressures
Consolidation Trends and Ecosystem Dependencies
The raised revenue threshold and acknowledgment of 160+ tracked vendors outside the Magic Quadrant suggest ongoing market consolidation. This consolidation creates strategic dependencies: as vendors increasingly rely on partner ecosystems for extended functionality, buyers must evaluate not just platform capabilities but ecosystem health, partner stability, and integration maturity.
The report’s emphasis on vendors’ “ability to cultivate a robust ecosystem of technology and service partners” (Gartner, 2024) acknowledges this reality but does not provide frameworks for assessing ecosystem risk. Vendor acquisition, partner conflicts, and technology standardization failures can rapidly transform competitive advantages into technical debt.
Budget Scrutiny and Value Demonstration Imperatives
The observation that “digital commerce initiatives are increasingly anchored to well-defined business objectives” with organizations “striving to boost conversion rates and foster customer loyalty, while simultaneously contending with budget constraints” (Gartner, 2024) reflects broader economic uncertainty. This environment favors vendors demonstrating clear ROI metrics and rapid time-to-value over those requiring lengthy implementations with uncertain outcomes.
However, the persistent challenge of “effectively measuring and connecting technological advancements to specific business outcomes” suggests the industry has not yet solved the attribution problem—linking platform investments to measurable business results remains more aspiration than operational reality.
Geographic and Deployment Model Considerations
Cloud Migration Imperatives
The prevalence of multitenant SaaS offerings across evaluated vendors reflects industry wide cloud migration. However, Adobe’s maintenance of both PaaS and SaaS environments, with no communicated end-of-support for legacy platforms, illustrates the practical complexity of cloud transitions for enterprise vendors with substantial installed bases.
Organizations evaluating vendors should scrutinize:
- Clear end-of-life roadmaps for legacy deployment models
- Feature parity commitments across deployment options during transition periods
- Migration tooling maturity and proven customer success cases
- Total cost of migration including services, testing, and potential business disruption
Geographic Availability and Localization
BigCommerce’s global availability on Google Cloud and Adobe’s presence across AWS and Microsoft Azure in all regions except China demonstrate infrastructure maturity (Gartner, 2024). However, geographic availability does not guarantee localization depth. Organizations with complex international requirements should validate support for:
- Regional payment methods and compliance requirements
- Multi-currency pricing with real-time exchange rate management
- Language and cultural adaptation beyond simple translation
- Region-specific tax calculation and regulatory reporting
Critical Omissions and Analytical Gaps
Security and Compliance Assessment Absence
Notably, the report provides minimal discussion of security capabilities, compliance certifications, or data protection features despite these being critical enterprise requirements. Organizations in regulated industries should demand supplementary vendor evaluation on:
- PCI DSS compliance and certification maintenance
- GDPR, CCPA, and other data privacy regulation support
- SOC 2, ISO 27001, and other security attestations
- Vulnerability management and incident response capabilities
Total Cost of Ownership Transparency
While the report mentions “lower TCO” as an evaluation factor, it provides insufficient guidance on comprehensive cost modeling. Organizations should account for:
- Platform licensing across different pricing tiers and consumption models
- Required third-party extensions and marketplace fees
- Implementation services and system integration costs
- Ongoing maintenance, upgrade, and support resource requirements
- Transaction fees and revenue-based pricing implications at scale
Recommendations for Enterprise Decision-Makers
Prioritize Proven Capability Over Roadmap Promises
Given the gap between vendor roadmaps (particularly around AI and agentic commerce) and production-ready capabilities, organizations should weight current functionality more heavily than future commitments. Request customer references with comparable scale, complexity, and use cases operating in production.
Demand Business Outcome Metrics
Insist vendors provide quantifiable business outcome data from comparable customer implementations, conversion rate improvements, average order value increases, customer lifetime value enhancements, operational cost reductions. Avoid accepting generic case studies or aggregate statistics that cannot be validated.
Evaluate Ecosystem Health Independently
Conduct independent assessment of vendor partner ecosystems through:
- Direct partner reference calls
- Technology partner financial health review
- Integration maturity testing for critical ecosystem components
- Assessment of partner concentration risk (over-reliance on few integrators)
Plan for Architectural Evolution
Whether pursuing monolithic or composable approaches, establish architectural governance frameworks that:
- Define clear interfaces and integration standards
- Establish vendor selection criteria for composable components
- Create migration paths preserving investment if vendor strategies shift
- Balance flexibility with operational complexity management
The final word
The Gartner Magic Quadrant for Digital Commerce reveals a market at an inflection point, transitioning from basic e-commerce capabilities toward comprehensive customer engagement platforms powered by AI and composable architectures. The 14% market growth and rising revenue thresholds indicate genuine market expansion and vendor consolidation (Gartner, 2024).
However, critical gaps persist between vendor aspirations and operational realities. The acknowledged difficulty in measuring AI’s business impact, the complexity of composable architecture management, and Adobe’s dual-platform maintenance challenges illustrate that market maturity does not eliminate fundamental execution risks.
Organizations evaluating digital commerce platforms should approach vendor selection with informed skepticism, demanding proof of operational capability rather than accepting roadmap promises. The “remarkable progress” in AI capabilities means little without demonstrated business outcomes. The “increased agility” of composable commerce provides limited value if offset by integration complexity exceeding organizational management capacity.
Ultimately, the right platform choice depends less on Magic Quadrant positioning than on alignment between vendor strengths, organizational technical capabilities, industry-specific requirements, and realistic assessment of implementation risk tolerance. The 160+ vendors outside this evaluation may provide superior fit for specific use cases, reinforcing that analyst research should inform rather than determine platform selection decisions.
Methodology Note
This analysis synthesizes information from the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Digital Commerce report with critical evaluation of claims, identification of analytical gaps, and contextualization within broader technology market trends. All direct attributions to Gartner cite the source report. Critical assessments represent independent analysis and should be validated through additional research and vendor due diligence appropriate to specific organizational requirements.














