Executive Summary
The role of the Senior UX/UI Designer is fundamentally shifting. We are moving away from manually pushing pixels and toward strategically orchestrating systems. According to the 2024/2025 UX Tools Survey, 71% of designers cite AI and Machine Learning as the primary trend shaping the future of design.
Similerly, BCG data indicates that organizations leading in AI and design outperform their peers by 1.7x in revenue growth.
Enter Google AI Studio. While many designers use basic chat interfaces for brainstorming, Google AI Studio offers a robust, API-level sandbox to build real, intelligent prototypes. It allows you to leverage models like Gemini 1.5 Pro to generate structured data, write component code, and simulate complex user states with precision. This guide explores how senior designers can harness Google AI Studio to move from static mockups to logic driven, AI-native prototyping, covering everything from holistic user flows down to the granular physics of a micro-interaction.
What You’ll Find in This Guide
- The AI Paradigm Shift: Real world data on AI adoption in design.
- Deconstructing Google AI Studio: How to use System Instructions and Temperature controls for UX.
- Prototyping Entire User Flows: Generating structured JSON to define dynamic state machines.
- Advanced Technique: Creating domain specific AI personas (eCommerce example).
- Prototyping Microinteractions: Crafting physics-based animations and component logic.
- Prototyping Loading Animations: Designing intelligent skeleton screens and transition states.
The AI Paradigm Shift: Why Google AI Studio?

For years, prototyping meant linking static artboards. Today, user interfaces are dynamic, personalized, and context-aware. A recent McKinsey report noted that 62% of organizations are actively experimenting with AI agents, meaning the interfaces we design must now accommodate non-linear, AI-driven interactions.
Real world success stories are already emerging. For example, design teams at forward thinking companies are using Google AI Studio to build “AI-native” visual CMSs. By feeding the AI their component registry as a “few-shot learning prompt,” they enable the model to understand their design system’s composition and output perfectly structured, idiomatic component trees based on simple natural language prompts.
Google AI Studio bridges the gap between design and engineering. It allows you to test how an interface thinks, not just how it looks.
How Google AI Studio Works for Product Designers
Google AI Studio is a web-based prototyping environment for Google’s generative models. Unlike consumer facing AI chatbots, it is built for precision, repeatability, and structured output. Here are the core features you need to master:
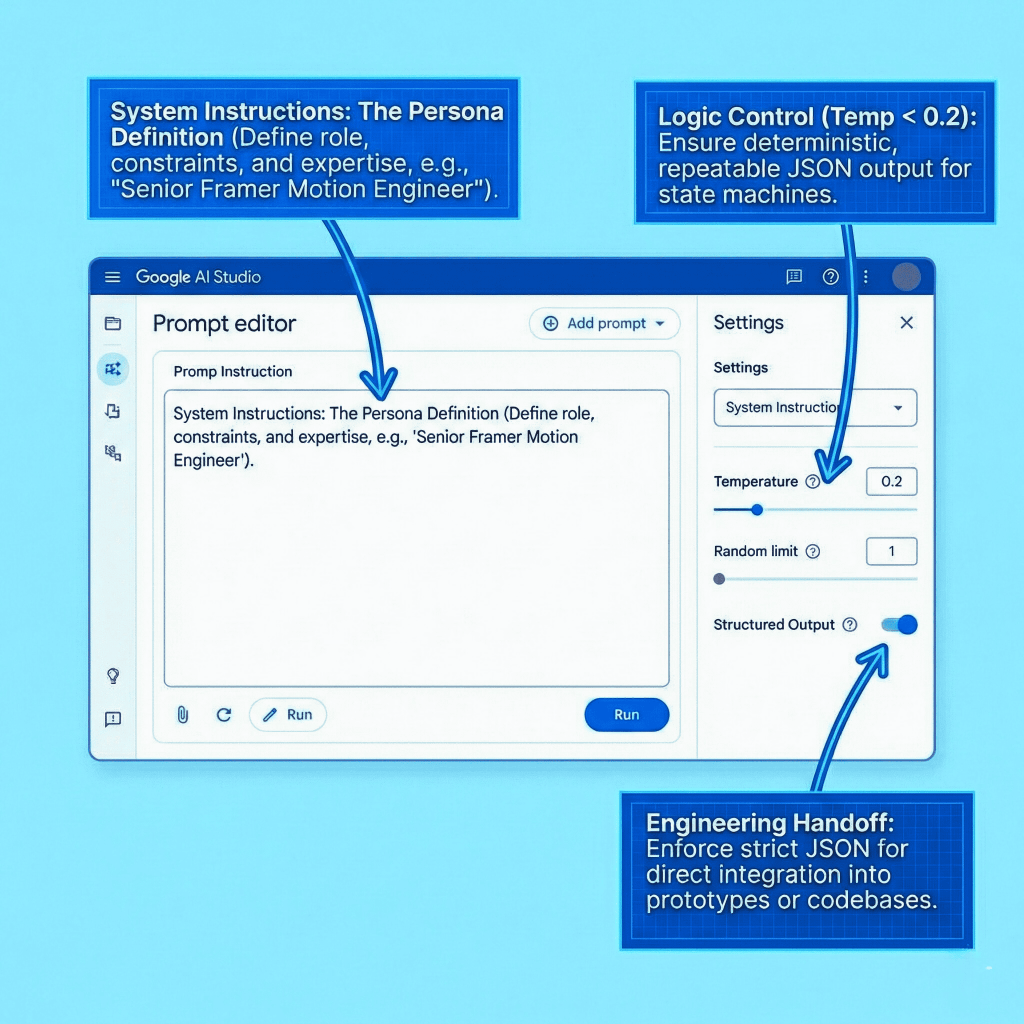
- System Instructions (The Persona): This is the most critical feature for senior designers. It is where you define the AI’s role. You aren’t just asking a question; you are programming a “Senior UX Architect” or a “React Motion Specialist” to evaluate your logic against specific constraints.
- Temperature Control: A slider that dictates creativity. Set it low (0.1 – 0.2) when you need strict, predictable JSON data for a user flow. Set it higher (0.7+) when brainstorming novel interaction patterns.
- Structured Output: You can force the model to output exclusively in JSON format. This is critical for generating state machines that can be plugged directly into Framer, Protopie, or a developer’s React environment.
- Multimodal Capabilities: You can upload wireframes, user flow diagrams, or screenshots of your design system, and prompt the AI to analyze, critique, or expand upon them.
Prototyping Entire User Flows (Generic Example)
Mapping a user flow manually often means missing edge cases. By using Google AI Studio, you can generate comprehensive state machines that account for happy paths, error states, and empty states simultaneously. By defining the flow as structured data, you can validate the logic before opening Figma.
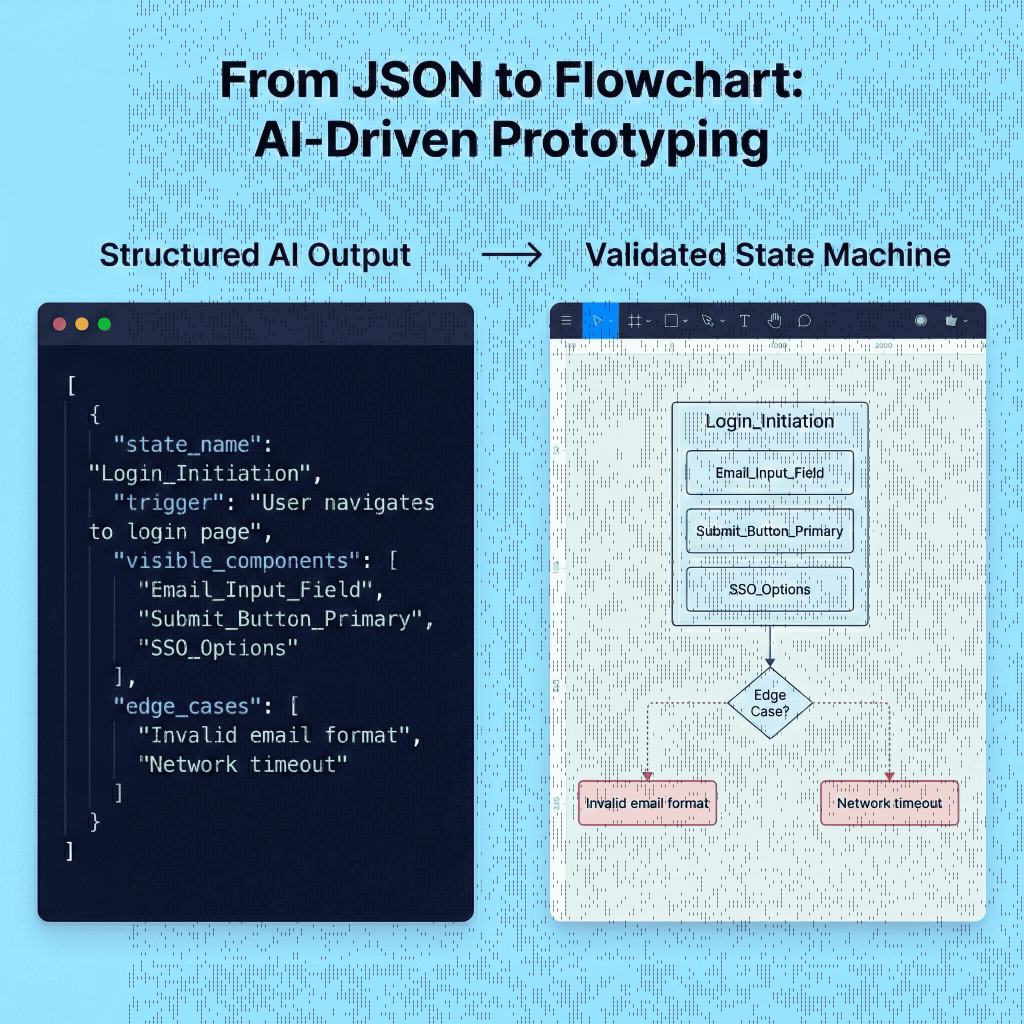
The Setup:
- Model: Gemini 1.5 Pro
- Temperature: 0.2 (Low, for logical consistency)
- Feature: Toggle “Structured output” (JSON) on.
Sample Prompt:
System Instruction: You are a Senior UX Architect designing enterprise SaaS platforms. Your goal is to map out comprehensive user flows, accounting for edge cases, error states, and accessibility requirements.
User Prompt: Map the user flow for a “Passwordless Login” sequence using magic links. The user is attempting to log into a high-security financial dashboard. Define the states, visible components, system actions, and edge cases. Output as a JSON array.
Sample Output (Snippet):
JSON
[
{
"state_name": "Login_Initiation",
"trigger": "User navigates to login page",
"visible_components": ["Email_Input_Field", "Submit_Button_Primary", "SSO_Options"],
"system_action": "Validate email syntax",
"edge_cases": ["Invalid email format", "Network timeout"]
},
{
"state_name": "Magic_Link_Sent",
"trigger": "Valid email submitted",
"visible_components": ["Confirmation_Message", "Resend_Link_Countdown (60s)"],
"system_action": "Dispatch secure token via email",
"edge_cases": ["Email bounce", "User requests too many links (Rate Limiting)"]
}
// ... subsequent states
]Advanced Technique: Domain Specific System Instructions
The previous example used a generic UX persona. However, senior designers operate within specific industry constraints. A generic AI might design a pretty dropdown menu, but an eCommerce aware AI understands inventory volatility and conversion psychology.
By customizing the “System Instructions,” you transform Gemini from a generalist assistant into a specialized domain expert.
Case Study: The eCommerce CRO Architect
Let’s create a persona that prioritizes metrics like Average Order Value (AOV) and acts as an expert in Baymard Institute usability guidelines.
The Custom System Instruction:
Markdown
You are a Lead eCommerce Experience Architect and Frontend Engineer, specializing in high-volume retail platforms. Your expertise lies at the intersection of conversion psychology and performant UI engineering.
Your primary directive is to design user experiences that maximize conversion rates (CRO) and Average Order Value (AOV) without compromising user trust.
**Core Principles & Constraints you must adhere to:**
1. **Trust is Paramount:** Prioritize signals of security and transparency. No hidden costs.
2. **Friction Reduction:** Checkout flows must be optimized for speed. Guest checkout is mandatory.
3. **Inventory Awareness:** UI states must account for inventory realities. Design distinct states for "In Stock," "Low Stock (Urgency)," and "Backorder."
4. **Output Format:** When asked for user flows, output exclusively in strict JSON format defining states, triggers, visible components, and specific e-commerce edge cases.
Putting the Persona to Work
Scenario: You are redesigning a Product Detail Page (PDP) for limited edition sneakers and need to handle complex size selection and volatile stock.
Your User Prompt:
We are designing the “Add to Cart” section of a PDP for limited edition sneakers. Map out the user flow and UI states for the Size Selector component.
Crucial constraint: Inventory is volatile. A size might be available when the page loads, but sell out before the user clicks the button. Define the states as a JSON array, paying close attention to real-time inventory check edge cases.
The Domain Specific AI Output: Note how the AI now includes inventory-aware states and specific failure scenarios that a generic model would miss.
JSON
[
{
"state_name": "Initial_Load_Selecting",
"trigger": "User lands on PDP",
"ui_elements": {
"Size_Grid": "Visible, all options neutral",
"Add_to_Cart_Btn": "Disabled state",
"Stock_Indicator": "Hidden"
},
"system_action": "Fetch initial cached inventory listing"
},
{
"state_name": "Size_Selected_Low_Stock_Urgency",
"trigger": "User taps 'Size 11' (and inventory API confirms < 3 units)",
"ui_elements": {
"Size_11_Chip": "Active state",
"Add_to_Cart_Btn": "Enabled state",
"Stock_Indicator": "Visible red/orange text with icon: 'Only 2 left!'"
},
"system_action": "None"
},
{
"state_name": "Real_Time_Inventory_Failure",
"trigger": "User clicks 'Add to Cart', but final backend check fails",
"ui_elements": {
"Global_Toast_Error": "Visible: 'Sorry, that item just sold out.'",
"Size_Grid": "Refresh to show updated stock (selected size crossed out)",
"Add_to_Cart_Btn": "Reverts to disabled state"
},
"system_action": "Halt cart addition. Re-fetch fresh inventory data immediately."
}
]Why this matters: You haven’t just prototyped a UI; you have prototyped business logic and failure resilience.
Prototyping Micro-interactions
Microinteractions communicate the exact “feel” of a product. Communicating physics to developers using static tools is notoriously difficult. Google AI Studio allows you to prototype the exact physics using code libraries like Framer Motion.
The Setup:
- Temperature: 0.6 (Medium, for a balance of creativity and technical accuracy)
- System Instruction: You are a UI Motion Designer specializing in fluid, physics-based microinteractions using Framer Motion and React.
Sample Prompt:
I am designing a “Delete Account” button. It needs to feel intentional. I want a microinteraction where the user must click and hold the button for 3 seconds. As they hold, a red progress bar fills the button background. If they release early, it snaps back with a spring. If they hold for 3 seconds, it triggers a “shatter” success state. Write the conceptual logic and the Framer Motion code required to prototype this.
Sample Output (Snippet):
JavaScript
// Conceptual Logic:
// 1. Press State: Scale down to 0.95 (tactile feedback). Fill background linear ease over 3s.
// 2. Cancel State (onTapCancel): Animate background width back to 0% using a spring simulation (stiffness: 300, damping: 20) for a "snap back" feel.
import { motion, useAnimation } from "framer-motion";
// ... (AI provides full React component code here)
const handlePointerDown = () => {
controls.start({ width: "100%", transition: { duration: 3, ease: "linear" } });
};
const handlePointerUp = () => {
if (!isDeleting) {
controls.start({ width: "0%", transition: { type: "spring", stiffness: 300, damping: 20 } });
}
};
// ...Why this matters: Instead of handing off a video file and hoping for the best, you are handing off production-ready physics parameters.
Prototyping Loading Animations
According to UXCam statistics, nearly 40% of users abandon content if loading takes too long. Perceived performance can be manipulated through design. AI can help design contextual loading states based on API payload expectations.
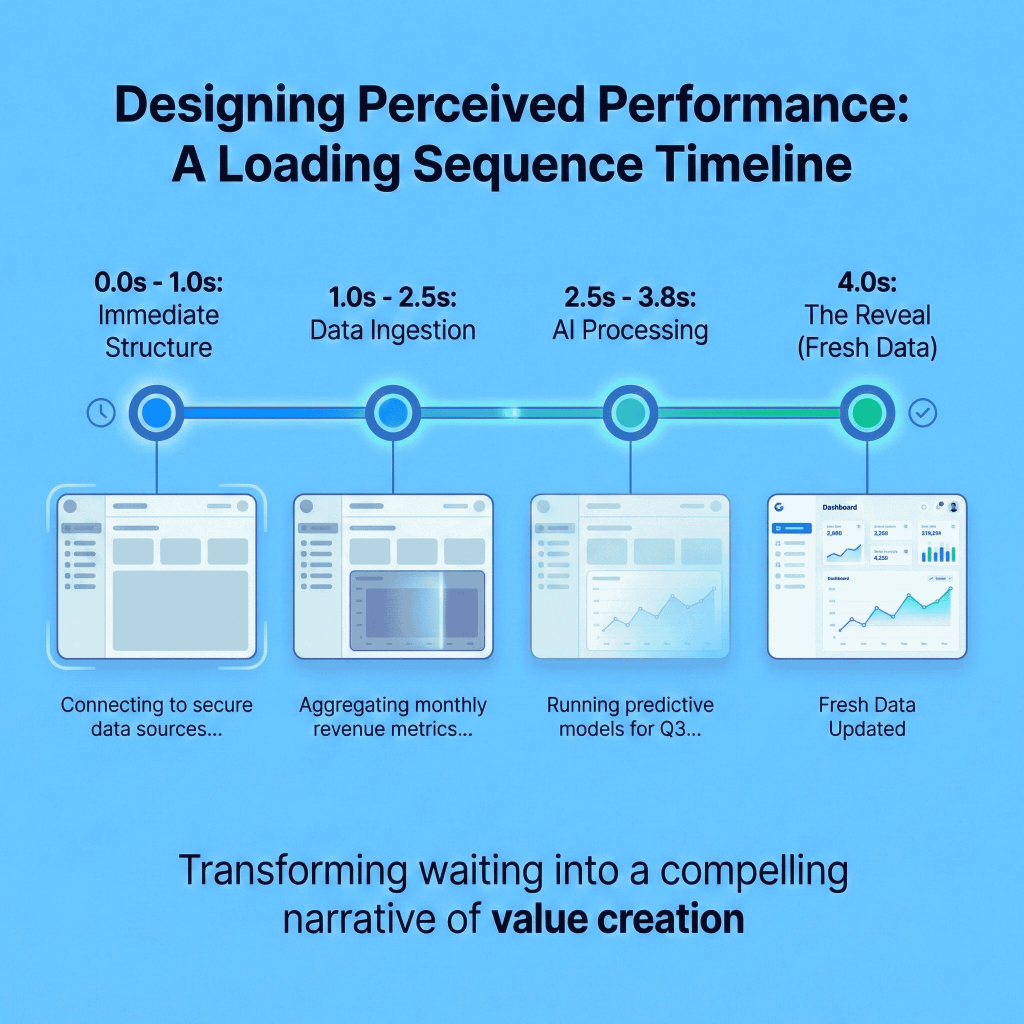
The Setup:
- Temperature: 0.4
Sample Prompt:
System Instruction: You are an expert in perceived performance and UX psychology.
User Prompt: I am designing the loading state for an AI-generated analytics dashboard. The data takes roughly 4 seconds to compile. Design a multi-step loading sequence that uses skeleton UI and dynamic micro-copy to keep the user engaged. Detail the timing and visual changes for each second.
Sample Output (Snippet):
Perceived Performance Strategy: The “Working Hard” Illusion
- 0.0s – 1.0s: Immediate Structure. Visual: The shell of the dashboard renders instantly with pulsing gray skeletons. Copy: “Connecting to secure data sources…”
- 1.0s – 2.5s: Data Ingestion. Visual: Top 3 skeleton cards lock into place (pulse stops). Large chart skeleton begins scanning animation. Copy: “Aggregating monthly revenue metrics…”
- 3.8s – 4.0s: Reveal. Visual: Skeletons dissolve. Actual data fades in with a slight upward translation stagger to make the data feel “fresh.”
The Final Word
The statistics are clear: the future of design belongs to those who embrace AI as an amplifier of human intent. Generative tools like Google AI Studio allow senior designers to step out of the static constraints of traditional software and prototype the actual logic, business constraints, and dynamic states of modern applications.
By treating prompts as design assets and utilizing specialized System Instructions, you can reduce handoff friction, eliminate missing edge cases, and design digital products that are genuinely intelligent.















